qNMR is quantitative NMR spctroscopy for the purity determination of organic molecules, based on the signal intensity is in direct proportionality with the number of protons contributing to the resonance.
Pro
Con
Good qNMR results:
Weighing of the reference and the sample prior to the qNMR measurements must be done with utmost accuracy. High-precision weighing and sample preparation. United States Pharmacopeia(USP) dictates a maximum uncertatinty error of 0.10%.
the reference substance and the sample must no react with each other or with the solvent.
S/N > 150 (using cryoprobe, using high field magnetic, more scans);
long enough relaxtion delay \frac{7}{3} \bullet T\_1;
Requirements to qNMR calibration standards
only substances with a very limited number of signals and of highest organic purity.
stable in solution and should not be chemically reactive.
they should not contain residual water.[ the presence of water can lead to line broadening or baseline distortion in many case]
solid reference should not be hhygroscopic and a liquid reference should not be volatile. (they must be no change in weighing value of greater than 0.02mg over a time period of 10min)1
a 1:1 signal intensity ratio of sample and internal standard is targeted.
not overlay
neither extremely toxic nor carcinogenic or mutagenic
Sigma Senior Scientist NMR applications Christine Hellriegel recommanded qNMR reference:
DMSO2[3.138ppm(s)] in D2O
Maleic acid(马来酸,顺丁烯二酸)[6.04ppm(s)] in D2O
KHP(邻笨二甲酸氢钾)[7.37-7.40ppm(m)] in D2O/NaOD
Calciumformate(甲酸钙)[7.5-8.5ppm] in D2O/DCl
Duroquinone(杜醌,四甲基对苯醌)[2ppm]in CDCl3
DMSO2[3.2ppm(s)] in DMSO-d6
Maleic acid in DMSO-d6
Benzoic acid[8.2-7.4ppm] in DMSO-d6
TCNB in DMSO-d6
3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid in DMSO-d6
Table 1 The Sigma-Aldrich qNMR toolbox comprises a selection of different high-purity CRM that cover the entire spectral range, allowing the quantification of almost any organic molecule by qNMR. The table gives an overview of spectral shifts, multiplicity, solubility and relaxation times in different solvents.
| NAME |
SHIFT(PPM)(PROTONS, MULTIPLICITY) |
D2O |
CDCL3 |
DMSO-D6 |
CD3OD |
CD3CN |
| Clcium formate |
7.6(2Hs) |
20s |
-- |
-- |
-- |
-- |
| Benzoic acid |
8.3-7.3(5Hm) |
-- |
4.4s |
3.2s |
3.3s |
5.8s |
| Duroquinone |
1.8-2.2(12Hs) |
-- |
3.2s |
2.7s |
4.2s |
4.6s |
| Dimethy terephthalate |
8.1(4Hs) |
-- |
4.0s |
3.1s |
4.7s |
5.7s |
| Potassium phthalate monobasic |
8.3-7.0(4Hm) |
2.4s |
2.4s |
-- |
3.4s |
-- |
| 3,5-Dinitrobenzoic acid |
8.8-9.2(3Hm) |
-- |
-- |
6.7s |
6.3s |
8.0s |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetrachloro-3-nitro-benzene |
7.6-8.7(1Hs) |
-- |
7.6s |
11.9s |
8.9s |
10.0s |
| Dimethyl sulfone |
3.0(6Hs) |
6.5s |
4.7s |
3.8s |
2.9s |
5.9s |
| Ethyl 4-(dimethylamino) benzoate |
1.3(3Ht) |
-- |
2.6s |
2.1s |
2.9s |
3.6s |
| Ethyl 4-(dimethylamino) benzoate |
3.0(6Hs) |
-- |
2.8s |
1.5s |
2.8s |
3.4s |
| Ethyl 4-(dimethylamino) benzoate |
4.3(4Hq) |
-- |
2.3s |
1.8s |
3.1s |
4.0s |
| Ethyl 4-(dimethylamino) benzoate |
6.7(2Hd) |
-- |
2.3s |
1.4s |
2.6s |
3.4s |
| Ethyl 4-(dimethylamino) benzoate |
7.8(2Hd) |
-- |
4.0s |
2.8s |
4.1s |
5.5s |
| Benzyl benzoate |
5.4(2Hs) |
-- |
2.5s |
1.4s |
2.9s |
3.5s |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetramethylbenzene |
6.9(2Hs) |
-- |
5.4s |
4.8s |
6.1s |
7.1s |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetramethylbenzene |
2.2(12Hs) |
-- |
3.4s |
2.6s |
4.3s |
4.5s |
| Dimethylmalonic acid |
1.3-1.4(6Hs) |
975ms |
-- |
604ms |
938ms |
-- |
| Maleic acid |
6.3(2Hs) |
6.3s |
-- |
3.1s |
4.2s |
6.1s |
| Octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane |
0.08(24Hs) |
--- |
2.6s |
-- |
4.4s |
3.5s |
This pdf shows their nmr peaks, Certified Standards for quantitative NMR The company SIGMA-ALDRICH offer a set of NIST traceable certified reference materials for use as internal standards in qNMR studies.
Methods
internal reference method;
external referencing approaches comprise NMR-tubes with coaxial inserts leading to a separation of analyte and standard;
electronic reference methods, e.g. ERETIC(Electronic Referencing to access in vivo Concentrations), PIG(Puls Into Gradient, ARTSI(Amplitude-corrected Referencing Through Signal Injection), QUANTAS(Quantification by Artificial Signal);
Theory
The intensity of the NMR signal is directly proportional to the number of protons that give rise to the signal. The purity determination of a substance can be calculated as follow:
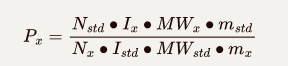
mx, WMx and Px represent the mass, molar masses and purity of the analysis;
m\_{std}, WM\_{std} and P\_{std} represent the mass, molar masses and assay of the standard;
I\_x and I\_{std} define the integrated signal area of the analyte and the standard, respectively.
N\_x and N\_{std} correspond to the number of protons in the integrated signal area of the analyte and the standard.
[weber2014]: M. Weber et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 93 (2014) 102-110

